Emacs startup file and configuration directory on Windows: where are init.el and .emacs.d?
Emacs relies on a startup file, usuallyinit.el (or back in the days, .emacs) placed in the .emacs.d folder within the user home directory.
If you are on a Unix based operating system, the HOME directory is a well defined concept and, most notably, a defined environment variable that Emacs can rely on to find out where .emacs.d (and hence init.el) or .emacs is.
On Microsoft Windows, althought the concept of user’s home directory is there, there is not a predefined variable that Emacs can use to its aim.
As a consequence, if you have your own configuration under
~/.emacs.d, such configuration will not be usable on Microsoft Windows in a straightforward manner. However, setting an HOME environment variable for Emacs to use is quite simple.
First of all, search in the
Start menu for an entry named like Manage environment variables, that will bring up a dialog window where you have to select the Environment variables button.
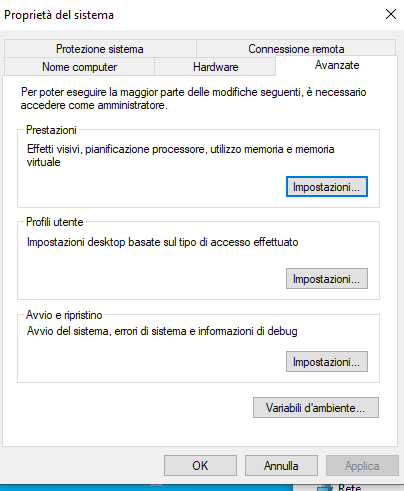
Then, add a new environment variable named, you guess,
HOME, that holds your own home directory, that on Microsoft Windows is something like C:\Users\<username>.
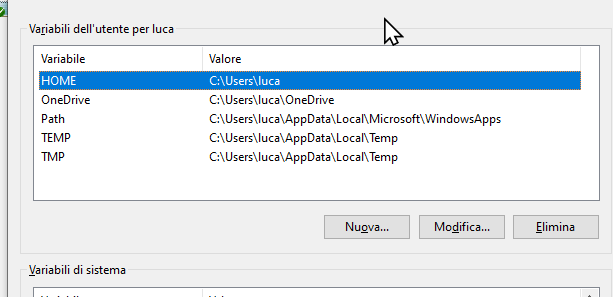
While you can make the
HOME variable to point to whatever you want, to avoid headaches, let it point to your own home directory.
Now you can place you
.emacs.d directory within the same home directory and have a nice day using Emacs on Microsoft Windows!